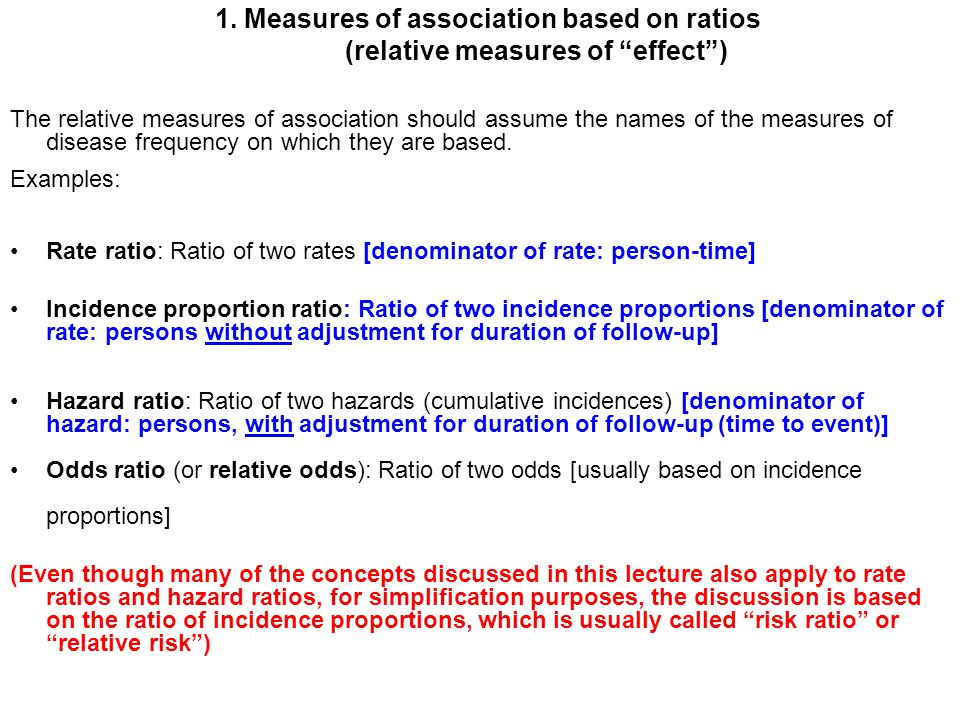
A rate ratio, ;Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r2ERA–EDTA Registry, Department of Medical Informatics, Academic Medical Center, University
1
Hazard ratio vs relative risk vs odds ratio
Hazard ratio vs relative risk vs odds ratio-The risk difference of A relative to B is 001, the risk ratio is 101 Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the risk ratioNow we don't gloss over the difference)




Hazard Ratios
A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsRelative Risk Reduction at time x 5 S EðxÞ2S CðxÞ 12S CðxÞ (Eq 1) It can be shown that this risk reduction is less than 1 2rat all postbaseline observation points and for any hazard ratio r < 1 (see Appendix) In other words, the relative reduction in risk of death is always less than the hazard ratio implies It is
There can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the likelihood of an event between two groups Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions 상대위험도(Relative Risk) vs 오즈비(Odds Ratio) Start BioinformaticsAndMe 1 상대위험도(Relative Risk;RR) vs 오즈비(Odds Ratio;OR) 상대위험도Interpretation of the Odds Ratio In the case of a rare disease, the population odds ratio provides a good approximation to the population relative risk The odds ratio can assume values between zero and infinity ( ) A value of 1 indicates no association between the risk




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
An odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make mention of handwaving;What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?Hazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram
When RR = 1, OR = 1The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal



Hazard And Hazard Ratio In Statistics




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Relation between the odds ratio, relative risk, and baseline risk Home Categories s My Tools About Leave message RSS category Bioinformatics tag Genetics "Odds ratios are not well understood as a measure of effect size, and conversion to relative risks by a simple calculation would improve understanding of findings" Relative Risk (Risk Ratio) • Expresses how many times more (or less) likely an exposed person develops an outcome relative to an unexposed person • Interpretation – RR > 1 Increased risk of outcome – RR = 1 No risk of outcome – RR < 1 Reduced risk of outcome 4Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Lorsque deux groupes sont en cours d'étude ou d'observation, vous pouvez utiliser deux mesures pour décrire la probabilité comparative d'un événement Ces deux mesures sont l'odds ratio et le risque relatif Les deux sont deux concepts statistiques différents, bien que tellement liés les uns aux autres




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies
Even an odds ratio;Measures of effect Relative risks, odds ratios, risk difference, and 'number needed to treat' G Tripepi1, KJ Jager2, FW Dekker2,3, C Wanner4 and C Zoccali1 1CNRIBIM, Clinical Epidemiology and Physiopathology of Renal Diseases and Hypertension of Reggio Calabria, Reggio Calabria, Italy; This brief communication will clarify the difference between a relative hazard and a relative risk We highlight the importance of this difference, and demonstrate in practical terms that 1 minus the hazard ratio should not be interpreted as a risk reduction in the commonly understood sense of the term




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk isA prevalence ratio, or ;
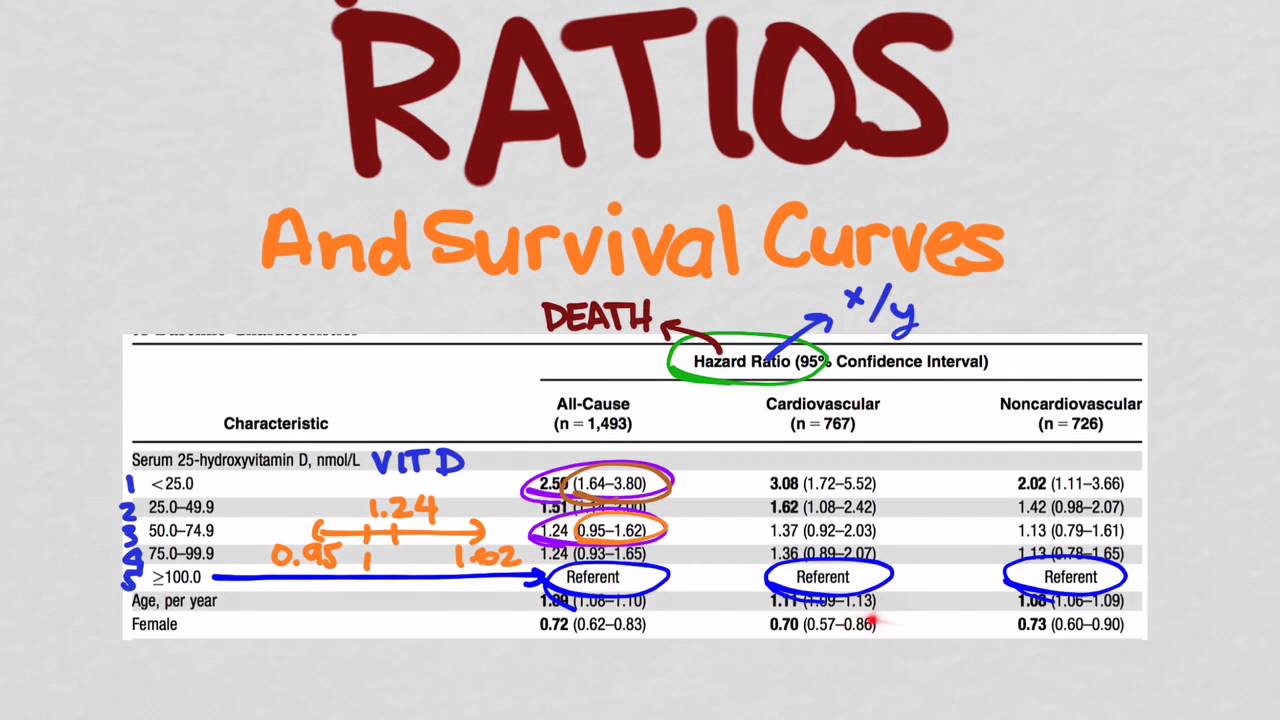



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Nonproportional Hazards For Time To Event Outcomes In Clinical Trials Jacc Review Topic Of The Week Sciencedirect
The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measure come risk is 01 or less, odds ratios and risk ratios agree well for risk ratio values ranging from 01 to 10 in all 3 figures When cumulative incidence is 10, the odds ratio is within 10% of the risk ratio for risk ratios ranging from 01 to 18 in Figure 1, from 055 to 10 in Figure 2, and from 04 to 25 in Figure 3 When cumulative inciIn the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measures




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ; While hazard ratios, relative risks, and odds ratios all show relative risk, there's plenty to distinguish them from one another, particularly around how they're calculated and interpreted That's why it's important to know which one is If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,– RiskThis implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400The absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskStart studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;




Challenges In The Design And Interpretation Of Noninferiority Trials Insights From Recent Stent Trials Sciencedirect




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect
StATS Odds ratio versus relative risk (created by ) Dear Professor Mean There is some confusion about the use of the odds ratio versus the relative risk Can you explain the difference between these two numbers?Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio et Risque Relatif (OR – odds ratio) et rapport de risque (HR – hazard ratio) « Propensity scorebased comparison of the graft failure risk between kidney transplant recipients of standard and expanded criteria donor grafts After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the study




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Estimation Of Absolute Risk Of Colorectal Cancer Based On Healthy Lifestyle Genetic Risk And Colonoscopy Status In A Population Based Study Gastroenterology
Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) groupThe method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simpleRelative risk = 52 103 = 050 Odds of severe exacerbation in Group A = 11/199 (ie a/b) Odds of severe exacerbation in Group B = 22/191 (ie c/d) Odds ratio = 11/199 22/191 = 048 ie (axd) (bxc) To look at the difference between the risk and odds ratio consider the same example (Ventolin vs placebo) but in a group of patients where




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
This video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratios In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities They will always agree on the direction of comparison In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have less heart disease than nonconsumers;



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
Exploiting the assumption that hazard ratios are asymptotically similar to relative risks, you can use exploit the formula recommendeed by Grant et al, BMJ 14 RR = OR / (1 p (p * OR) where RR is the relative risk, OR is the odds ratio, and p is the control event rate, which leads to the following OR = ((1 p) * RR) / (1 RR * p)This is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both rows and columns gives Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a disease




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Is still NOT the hazard ratio, as it is not a ratio of conditional probabilities Maybe the easiest way to understand that a hazard ratio cannot be equal to the relativerisk for any timetis to realize that eventually everybody dies, so the relative risk willapproach 1 with time, even though the hazard ratio is constantSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4 Relative risks versus odds ratios Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus for the prevention of any diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use in hospital A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial study design was used




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And
The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regret



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




How Did Researchers Calculate The Hazard Ratio Cross Validated




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



1



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
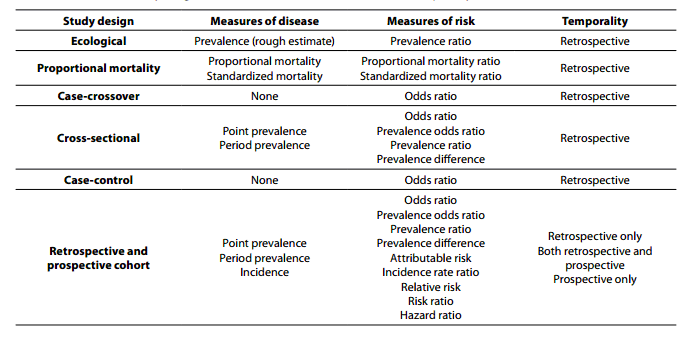



Observational And Interventional Study Design Types An Overview Biochemia Medica




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download




Reading Understanding Medical Studies On Deadline



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Odds Ratio Article




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet




Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Lincom Stata
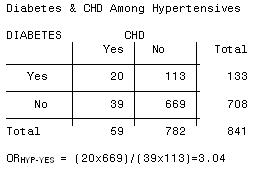



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507



1




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



1
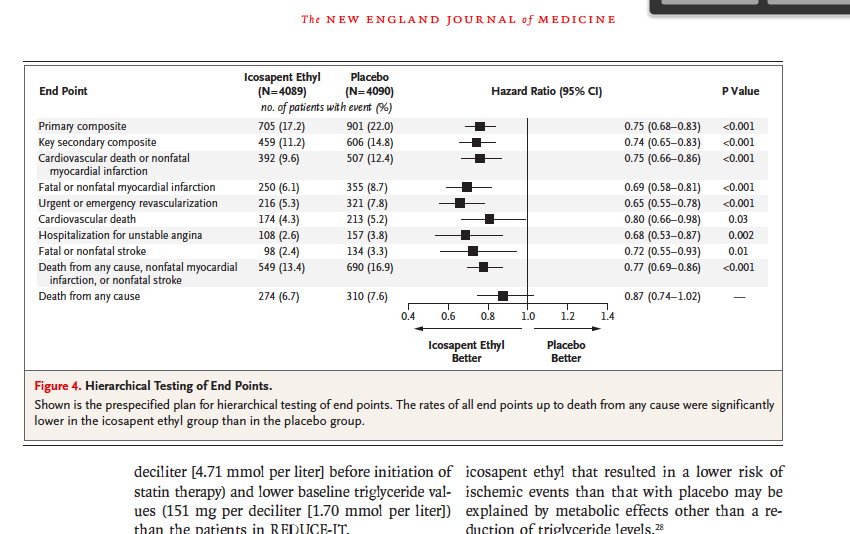



State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com




New Resource Can Help You Assess Hazards And Risks And Odds Ratios Laptrinhx News




Hazard Ratios




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Pierfilippo De Sanctis Pfdesanctis Profile Pinterest




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
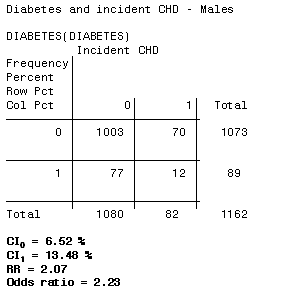



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
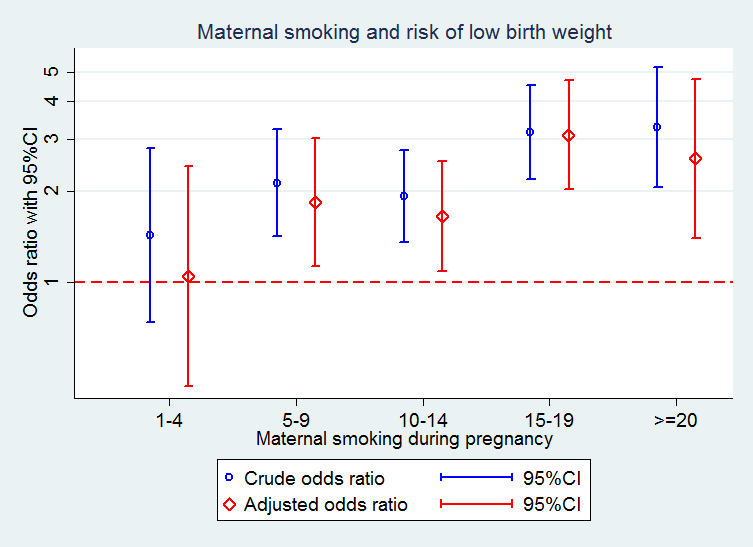



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk




Math3010 Week 6




Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11



Epidemiology Stepwards




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




Why Statistics To Understand Studies In Clinical Journals




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Pdf Data Analysis Of Epidemiological Studies Part 11 Of A Series On Evaluation Of Scientific Publications Semantic Scholar



1




Confidence Intervals And P Values



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
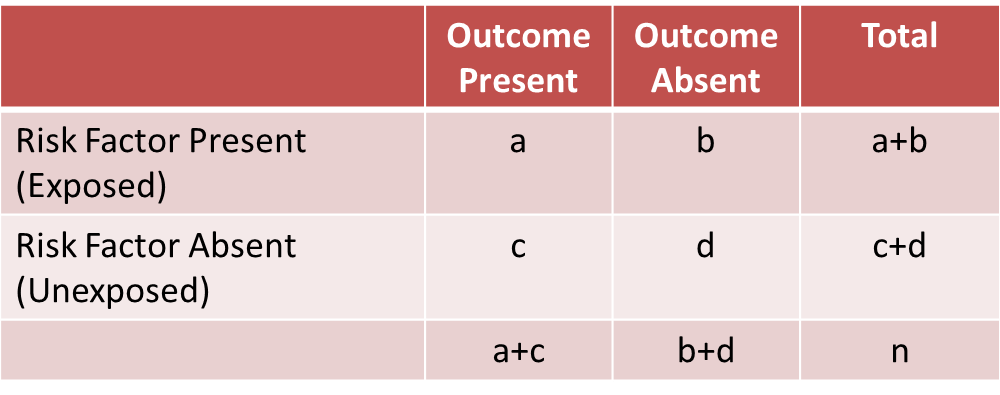



A Stratified Analysis




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect
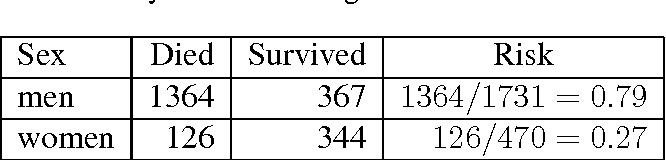



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
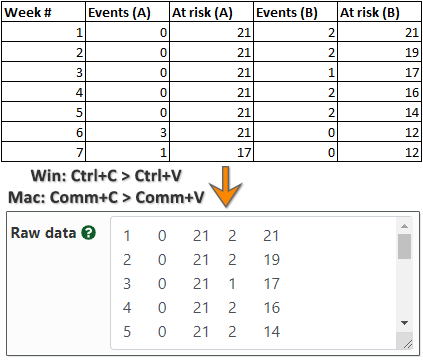



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿